BEST HOSPITAL FOR PILES SURGERY
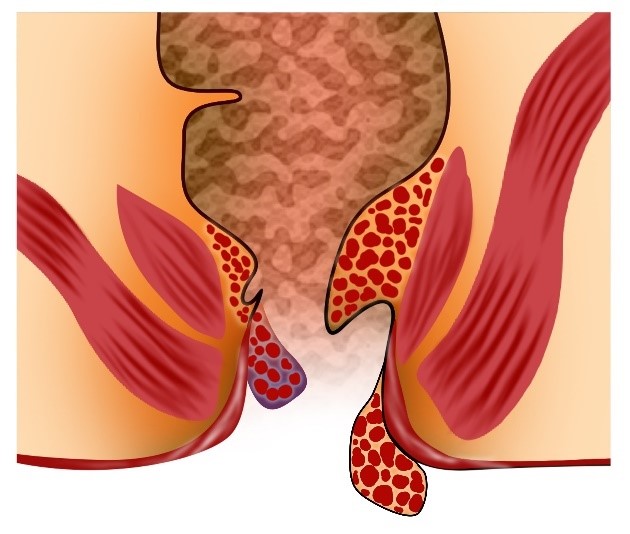
Piles, also known as hemorrhoids, are particularly abundant within the anal canal or around the anus (external hemorrhoids). Damage to swollen anal or rectal tissue can result in bleeding and pain. Piles frequently do not cause symptoms, and people are unaware that they have them. Symptoms that may appear include bleeding after a bowel movement, Bottom itch, a lump in the anal canal or near the anus, Anxiety, pain, and swelling There is a slimy mucus discharge after a bowel movement. Piles usually go away on their own, but in the meantime, dietary changes and simple treatments may be recommended to relieve symptoms. Depending on their location, severe piles may necessitate more intensive treatment. Banding, Sclerotherapy, and Electrotherapy are non-surgical options for treating piles in the upper two-thirds of the anal canal. However, piles in the lower third, closest to the anus, will necessitate anesthetic surgery due to the number of pain-sensing nerves in this area, making non-surgical techniques too painful. Although piles are usually treatable with lifestyle changes, creams, ointments, or non-surgical techniques, surgery is required in one out of every ten people. The most common surgical procedures used to treat piles are haemorrhoidectomy, stapling, and haemorrhoidal artery ligation.
- BEST HOSPITAL FOR PILES SURGERY IN PALAM
- BEST HOSPITAL FOR PILES SURGERY IN HARI NAGAR
- BEST HOSPITAL FOR PILES SURGERY IN MOTI NAGAR
- BEST HOSPITAL FOR PILES SURGERY IN TILAK NAGAR
FOR MORE DETAILS PLEASE CONTACT US AT 9891682297.
| Tags: |
